Functional Group
The carbon chain that came from the alcohol is given the suffix "-yl" as if it is a side chain.
The other carbon chain (containing the C=O bond) is given the suffix "-anoate". This is also the suffix for a salt made from a carboxylic acid.
Esters can be made by reacting alcohols with either:
- carboxylic acids, with concentrated sulfuric acid and heat, OR
Reactions
HYDROLYSIS
Acidic and alkaline conditions can break the ester bond:
Acidic Conditions
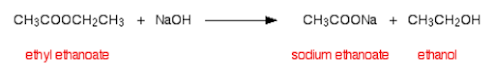
Alkaline Conditions - note the different products!
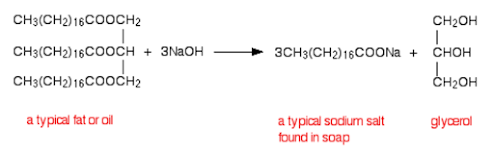
SAPONIFICATION
This is a fancy name for making soaps. Fatty acids are esters, and can be hydrolysed to make soaps:
Properties
Esters are insoluble in water. This is because they have a large non-polar part and cannot form hydrogen bonds with water. They do hydrolyse in water, forming the alcohol and carboxylic acid.
Their melting and boiling points are comparable to similar-sized aldehydes and ketones.






No comments:
Post a Comment