Acid chlorides are much more reactive than their carboxylic acid counterparts. Therefore, they are often preferred for industrial processes.
Functional Group and Nomenclature
The suffix for acid chlorides is "-anoyl chloride"/
Preparation
Acid chlorides are prepared by reacting a carboxylic acid with thionyl chloride:
Reactions
All reactions of acid chlorides produce HCl gas as a byproduct, except amide formation (which only liberates HCl gas when a primary amide is made, with heat provided).
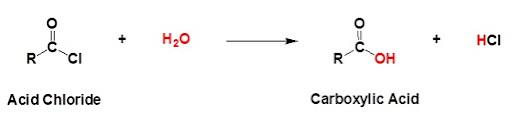
WITH WATER
Acid chlorides do not dissolve in water because they react with water molecules instead:
Reacting with ammonia and heat will produce a primary amide, with ammonium chloride as a byproduct.
Reacting with amines will produce secondary and tertiary amides, with an amino salt as a byproduct.





No comments:
Post a Comment